A rainwater pump is an essential component of rainwater harvesting systems. These pumps are designed to effectively transport rainwater from storage tanks or collection points to various applications such as irrigation, toilet flushing, and laundry. By utilizing a rainwater pump system, you can harness the power of nature to meet your water needs sustainably.
With their powerful mechanisms and reliable performance, rainwater pumps ensure a steady flow of water, regardless of the season or weather conditions. They are specifically engineered to handle the unique characteristics of rainwater, such as debris and contaminants, ensuring optimal functionality and longevity. Whether you are a homeowner looking to reduce water consumption or a commercial establishment aiming to adopt eco-friendly practices, investing in a high-quality rainwater pump system is a wise choice that promotes water conservation and helps you make the most of this precious resource.

What is a Rainwater Pump?
A rainwater pump is a mechanical device connected to various applications' rainwater storage tanks or collection points. It plays a vital role in rainwater harvesting systems by efficiently utilizing collected rainwater for different purposes.
The primary function of a rainwater pump is to create pressure and deliver water at a desired flow rate to meet specific water demands. These demands may include irrigation for gardens or crops, toilet flushing, laundry, or other non-potable uses. Rainwater pumps are typically electrically powered but can also be operated manually or through solar energy.
What to Consider When Selecting a Rainwater Pump
When choosing a rainwater pump for your harvesting system, it's essential to consider several factors. Here are key considerations to keep in mind:
1. Flow Rate
The flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM), determines how quickly the pump can deliver water. Assess your water demands and choose a pump with a flow rate that meets your requirements. Consider both peak demand scenarios and average usage to ensure the pump can handle the desired water volume.
2. Pump Power and Pressure
The required pressure or total dynamic head is arguably as important as the flow rate. If you have a below-ground installation and need to pump to the 7th floor of a building, you need enough Total Dynamic Head (TDH) to push the water to overcome that height difference, otherwise, the water will never reach that portion of the building.
Different applications require varying levels of water pressure. Determine the required pressure for your intended use, whether for irrigation, household needs, or commercial applications. Additionally, consider the power source available for the pump—electricity, solar, or manual—and choose a pump that aligns with your preferences and accessibility. If you need your pump for rainwater harvesting to provide enough pressure to mimic that of a normal residential system, you'll need a rainwater pump that is able to produce 45-60 PSI.
3. Pump Size and Capacity
The physical size and capacity of your rainwater pump systems should match the available space for installation. Assess the pump's dimensions and ensure it fits your designated location, whether indoors or outdoors. Additionally, consider the pump's capacity in terms of the maximum amount of water it can handle to meet your demand.
4. Pump Efficiency
Look for rainwater pumps with high energy efficiency ratings, as they minimize power consumption and reduce operating costs. Energy-efficient pumps help optimize the rainwater harvesting system's overall performance, allowing you to save resources and contribute to sustainability.
5. Durability and Materials
Consider the durability and construction materials of the rainwater pump. Look for corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or high-quality plastics, that can withstand exposure to rainwater and various environmental conditions. A durable pump ensures long-term reliability and reduces the need for frequent maintenance or replacements.
6. Pump Controls and Automation
Some rainwater tank pumps come with advanced control features, such as adjustable speed settings or automation options. These features provide greater flexibility and allow you to customize the pump's operation based on your specific needs. Automation can also enable seamless operation and monitoring integration with other system components.
7. Electrical Requirements
This is probably the most straightforward of the bunch: what electrical characteristics do you have available? Some flow rates and pressures are only able to be accomplished with higher voltage and three-phase power. For most residential applications, 115V/1 phase/60 Hz or 230V/1/60Hz power will suffice as these pumps are providing flow and pressure at rates similar to a city or well line.
8. Warranty and Continuing Support
Check the manufacturer's warranty and after-sales support options. A reliable warranty ensures protection against potential defects, while comprehensive after-sales support can provide technical assistance and troubleshooting guidance when needed.
Shop Rainwater PumpsA Closer Look at Pumps for Rainwater Tanks
Flow rate and the pump curve are closely related and play a significant role in understanding the performance of a pump within a rainwater harvesting system. Let's take a closer look at these concepts.
Rainwater Harvesting Pump Flow Rate
Flow rate, also known as the pump capacity, refers to the volume of water a pump can deliver per unit of time. The flow rate is a crucial factor to consider when selecting a rainwater pump as it determines how quickly water can be supplied to the intended applications.
Here are a few examples of flow rate requirements for rainwater collection pumps:
- Garden Hose: 2-4 gallons per minute
- Toilets: 1.6 gallons per flush
- Washing Machine: 2 gallons per minute
Make sure to account for all of your potential combined uses and choose a rainwater collection pump that can accommodate the maximum total flow rate.
Pressure or Total Dynamic Head
The required pressure or total dynamic head is arguably as important as the flow rate. If you have a below-ground installation and need to pump to the 7th floor of a building, you need enough Total Dynamic Head to push the water to overcome that height difference. Otherwise, the water will never reach that portion of the building.
Likewise, if you need your rainwater harvesting pump to provide enough pressure to mimic that of a normal residential system, you'll need a rainwater pump that is able to produce 45-60 PSI.
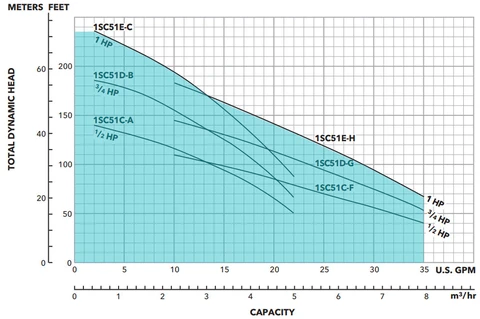
What Size Rainwater Pump Do I Need? Understanding the Pump Curve
Now that you know your flow rate and required pressure/TDH, you'll need to select one of the different types of rainwater tank pumps that can accommodate both. Let's take a look at a sample pump curve.
For example, let's say you need 25 Gallons per minute at 100' TDH. The 1/2 HP and 3/4 HP options do not quite get there, but the 1 HP pump (1S51E-H) does and would be the pump you need to select.
Install Location and Pump Style
This is typically a very project-specific factor. The installation location typically refers to whether or not the pump is installed inside the storage tanks (submersible water pumps) or outside the tanks (boosters/jets). Each rainwater harvesting pump style has its own benefits.
For example, a submersible rainwater collection pump is often quieter as it is submerged in the water tank, is out of sight/not in the floor space and allows for constant pump access to water (as long as the float switch is used for dry run protection). However, on the negative side, it must be disconnected and removed in freezing conditions, is more difficult to maintain, and typically requires stainless steel components for long-term submersion, which could affect cost.
A booster/jet pump is easy to maintain, can be disconnected easily during freezing conditions, and can sometimes be more cost-effective with lower-cost materials since it is not submerged. However, they can sometimes be noisy, take up floor space, and lose their prime if not in a flooded suction state.
Submersible Rainwater Harvesting Pump Example

Booster/Jet Rainwater Pump Example

There are various types of pumps to choose from. You can order a suction jet pump, or a submersible pump. It’s important to do your research before jumping in and purchasing one or the other.
View Our Pump OptionsHow Long Do Rainwater Pumps Last?
The lifespan of a rainwater pump can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the pump, the operating conditions, maintenance practices, and the specific model or brand. On average, a well-maintained and properly installed rainwater pump can last anywhere from 10 to 15 years.
Regular maintenance is crucial to prolonging the lifespan of a rainwater pump. This includes cleaning the pump and removing any debris or sediment that may accumulate, inspecting and replacing worn-out parts as needed, and ensuring proper lubrication of moving components. Following the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule and guidelines will help optimize the pump's performance and extend its longevity.
Get a Water Tank Pump System From RMS
A pump for rainwater harvesting can revolutionize your residential or commercial site. By tapping into Earth's most natural resource using a rainwater pump system, you can decrease your environmental impact while saving money on water costs. If you still need help choosing which types of rainwater pumps are right for you, contact us and we’d be happy to help you size up a water tank pump system for your rainwater harvesting project.
Contact Us Today



