The purpose of rainwater harvesting extends far beyond mere water collection; it embodies a strategic approach to managing a crucial natural resource.
Environmentally, rainwater collection is pivotal in reducing the demand on our overburdened water systems. By capturing rainwater, we can lessen the load on municipal water supplies, especially in areas where water scarcity is a growing concern. This practice ensures a supplementary water source during dry spells and contributes to replenishing groundwater levels, a critical aspect of maintaining the ecological balance.
In the broader scope of sustainable development, rainwater harvesting is a key player. It aligns with the principles of sustainable living by promoting the efficient use of water resources and decreasing the environmental footprint of human activities. The practice encourages a more responsible and mindful approach to water usage, fostering a culture of conservation and awareness. By integrating rainwater harvesting into urban planning and building design, cities and communities can become more resilient to increased precipitation variability and urban flooding.
On a micro level, uses for collected rainwater include:

Understanding how rainwater harvesting works requires a grasp of its basic principles and the mechanics of rainwater collection, all within the broader context of the natural water cycle.
At its core, rainwater harvesting is a process that intercepts, collects, and stores rainwater for future use. The principle is straightforward: capture rainwater where it falls rather than allowing it to run off. This is typically done using a catchment area, such as a rooftop, which is the primary surface for collecting rainwater. From here, the water is channeled through gutters and downspouts, directing it into a storage vessel, like a tank or barrel. The stored water can then be filtered and pumped for various uses, ranging from irrigation and landscaping to flushing toilets and drinking.
To appreciate the role of rainwater harvesting, you must consider the natural water cycle, comprising evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and collection. Rainwater harvesting taps into this cycle at the precipitation stage. When rain falls, a portion of it naturally seeps into the ground, replenishing aquifers, while some evaporates back into the atmosphere. The rest becomes surface runoff, which can lead to erosion and water pollution as it collects and carries various contaminants.
By collecting rainwater, we capture a portion of this precipitation before it hits the ground, thus reducing runoff and its associated problems. This intervention allows us to immediately and directly use the rainwater, easing the demand for groundwater and surface water resources.

Rainwater harvesting offers many benefits spanning environmental, economic, and social factors, making it an invaluable practice.
One of the most significant environmental advantages of collecting rainwater is its ability to reduce runoff. Urban runoff often carries pollutants like oils, pesticides, and sediments into water bodies, damaging aquatic ecosystems. When rainwater is collected, this runoff is significantly reduced, minimizing its ecological impact. Additionally, rainwater harvesting aids in recharging groundwater levels. In urban areas, where impermeable surfaces are abundant, rainwater often fails to infiltrate the ground, leading to depleted groundwater. Harvested rainwater can artificially recharge these aquifers, helping maintain the delicate balance of our groundwater systems.
Using harvested rainwater for non-potable uses, such as irrigation and flushing toilets, reduces water extraction from sensitive ecosystems. This practice is critical in regions experiencing drought or water scarcity, where every drop saved contributes to the environment's overall health.
From an economic perspective, rainwater harvesting can significantly cut costs. By using harvested rainwater for various purposes, businesses and households can reduce their reliance on municipal water supplies, lowering water bills. This is especially beneficial in regions with high water tariffs or where water is metered. Furthermore, for agricultural and industrial users, rainwater harvesting can be a cost-effective alternative to relying solely on purchased water, reducing operational costs and increasing competitiveness.
Socially, rainwater harvesting plays a crucial role in promoting water conservation awareness and community engagement. It serves as a tangible demonstration of sustainable living, inspiring individuals and communities to actively manage their water resources. Educational initiatives centered around collecting rainwater can foster a culture of conservation, making individuals more mindful of their water usage and its broader impacts.

A rainwater collection system consists of several key components, each playing a crucial role in efficiently capturing, storing, and using rainwater. Understanding these components is essential for anyone considering a rainwater harvesting system.
The catchment area of a rainwater harvest system is the primary surface where rainwater is collected. In urban settings, rooftops serve as the most common catchment area. They offer a wide, unobstructed surface that is ideal for capturing rainwater. In rural or open land areas, the catchment can also include ground surfaces like fields or landscaped areas specifically designed for rainwater collection. The efficiency of a catchment area depends on its size, the material it's made from, and its cleanliness.
Once rainwater hits the catchment surface, it must be directed to the storage vessel. This is where the conveyance system, consisting of gutters and downspouts, comes into play. Gutters line the edges of the rooftop, collecting the water and leading it to downspouts. These downspouts then channel the water down and away from the building structure, often into a filtration system before it reaches the storage tanks.
Storage vessels are perhaps the most critical component of a rainwater collection system. These can range from simple barrels to large rainwater storage tanks. The choice of storage facility depends on the intended use of the collected water, the amount of rainfall, and the space available.
Before the harvested rainwater can be used, it often requires treatment to ensure it is safe for its intended use. This treatment can include rainwater filtration systems to remove debris and disinfection systems to eliminate harmful microorganisms. After treatment, the water is distributed through pumps and pipes, which can be integrated with existing plumbing systems for indoor or outdoor use.
Each component of a rainwater collection system is vital to its overall effectiveness and efficiency. From the initial capture of rainwater on catchment surfaces to the conveyance, storage, treatment, and eventual distribution, every step is critical in ensuring that the harvested rainwater is utilized to its fullest potential. Rainwater Management Solutions understands these components and delivers rainwater harvesting systems that are functional and sustainable.

Each rainwater collection system can be categorized into one of several types suited to different needs and environments. The most common types include rooftop rainwater harvesting, surface runoff harvesting, and in-situ rainwater harvesting methods.
This is the most prevalent form of rainwater harvesting, especially in urban areas. In this system, the roofs of buildings serve as the catchment areas for collecting rainwater. The simplicity of this method lies in its use of existing structures, requiring minimal additional infrastructure. Water collected from rooftops is channeled through gutters and downspouts and stored in tanks or barrels. Rooftop harvesting is particularly effective for domestic use, providing a supplementary water source for activities like gardening, flushing toilets, and even drinking.
Stormwater collection and reuse is Becoming more broadly used due to the increase in impervious surfaces. This method involves collecting rainwater from surfaces like land, gardens, and paved areas. The collected runoff water can be stored in ponds, reservoirs, or underground tanks. This type of system helps conserve water and prevents soil erosion and flooding caused by surface runoff.
Rainwater harvesting detention refers to techniques that allow rainwater to infiltrate the ground and augment groundwater directly. This method includes practices like creating percolation pits, trenches, and recharging wells. These structures capture rainwater and allow it to percolate into the soil, restoring the groundwater table. In-situ methods are crucial in areas with declining groundwater levels and can be integrated into both urban and rural landscapes.
Each type of rainwater collection system offers unique benefits and should be selected based on the area's specific requirements, such as climate, topography, and the intended use of the harvested water. Rainwater Management Solutions has the skill and expertise to design the best rainwater harvesting system for your needs.
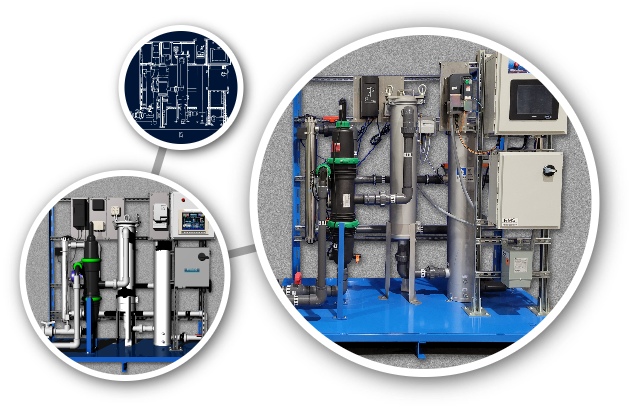
Rainwater harvesting is rich with a blend of traditional techniques and modern technological advancements, each contributing to more sustainable and efficient water management practices.
Traditional rainwater harvesting techniques have been honed over centuries, tailored to suit different climates and geographical conditions. In rural India, for example, "johads" — small earthen check dams — are used to capture and store rainwater, recharging groundwater and supporting agriculture. In arid regions, "berms" or small crescent-shaped mounds are constructed to catch and hold rainwater for crops. These traditional methods often require minimal technology and rely on locally available materials, making them cost-effective and accessible.
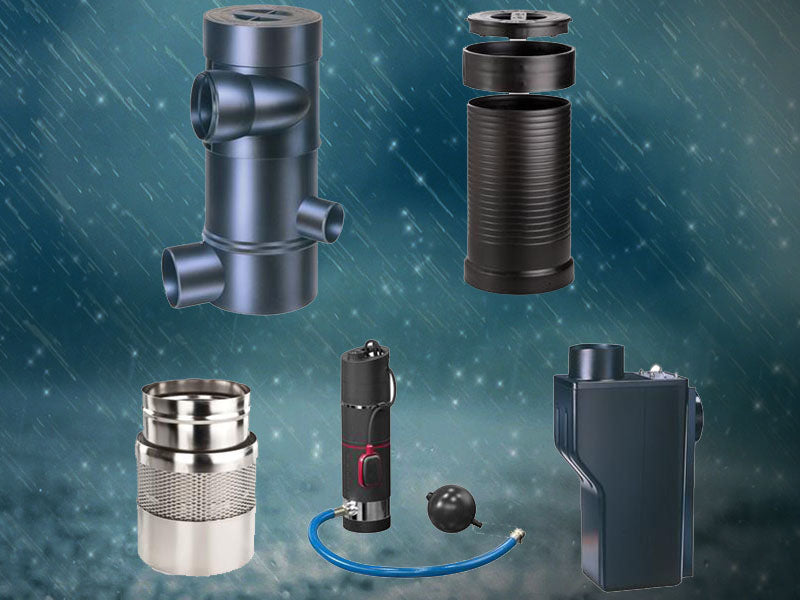
Modern rainwater harvesting techniques incorporate advanced technology to enhance efficiency and expand usability. These include using high-quality, UV-resistant storage tanks to prevent algae growth and ensure long-term water storage. Gutter and downspout systems have also evolved, with materials and designs that reduce blockages and maintenance requirements. Rainwater Management Solutions provides a full complement of rain collection products, allowing you to take full advantage of today's rain harvesting technologies.
Significant progress in water purification technologies has made it feasible to use harvested rainwater for a broader range of purposes, including drinking. Rainwater Management Solutions offers filtration and UV sterilization products that can be integrated into your rainwater collection system to ensure water safety and quality.

Implementing a rainwater collection system involves several critical steps, from initial planning and design to installation and ongoing maintenance. Each phase is crucial for ensuring the system's efficiency, longevity, and safety.
The first step is thorough planning, which involves assessing the need and capacity for rainwater harvesting. This includes calculating the catchment area (usually the rooftop), estimating the average rainfall, and determining the storage capacity required based on usage needs. It's also essential to consider the local climate and weather patterns. The design should incorporate suitable materials for the catchment surface, gutters, and storage tanks, considering factors like durability and water safety. Additionally, the design must include appropriate filtration and purification systems that align with the intended use. Rainwater Management Solutions excels at designing rainwater collection systems that meet our customers' needs.
Once the design is finalized, the next step is installation. This process starts with setting up the catchment area, which, in most cases, is the existing rooftop. Gutters and downspouts must be installed or modified to effectively channel the water into the storage system. Care must be taken to ensure these components are correctly aligned and secured to prevent leaks and blockages. The storage tank, which can be above or below ground, should be positioned considering accessibility for usage, maintenance, and safety.
Installing a filtration and purification system is critical to ensure the water meets required standards. These systems must be installed according to manufacturer guidelines and local health regulations. Finally, integrating the system with existing plumbing, especially for indoor use, requires careful planning and execution.
Our systems are renowned for being low maintenance; minimal effort can help ensure the long-term success of your rainwater collection system. This includes cleaning the catchment area and gutters to remove debris, checking the prefiltration, which can contaminate the water or cause blockages. The storage tanks should be inspected regularly for leaks, cracks, or algae growth. Post-tank filtration and purification systems also require routine checks and maintenance to keep them functioning effectively.
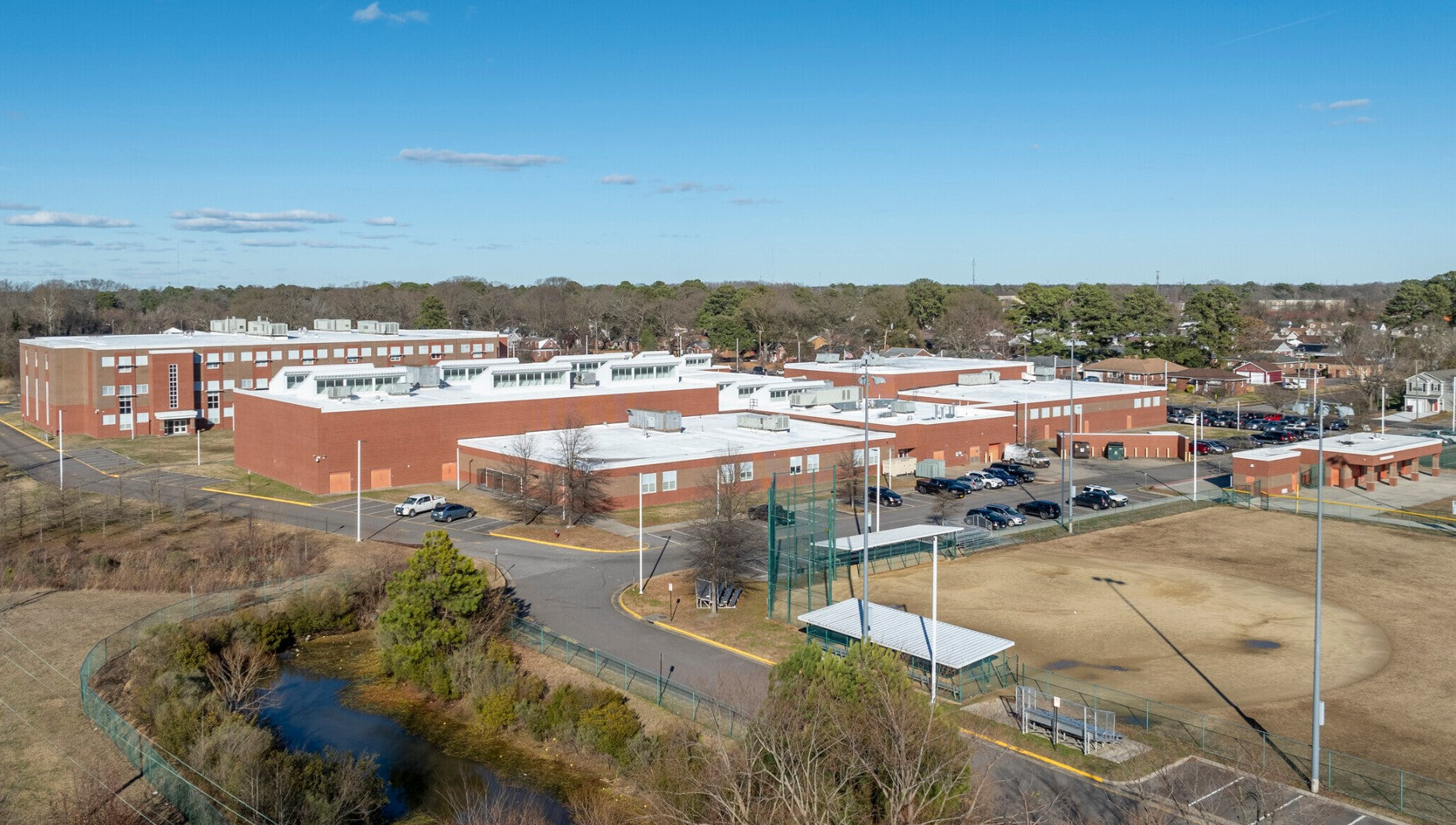

The effectiveness of rainwater harvesting is highlighted through various case studies and success stories from around the world, demonstrating a significant impact on water conservation.
In Virginia Beach, Virginia, Oscar Smith Middle School overcame its water scarcity challenges through an effective rainwater collection system. The school reduced its reliance on municipal water for non-potable uses and set an example for other schools in the Chesapeake Bay area in managing water resources sustainably.
The U.S. Federal Energy Management Program has identified rainwater collection as a viable option for federal facilities looking to reduce their reliance on freshwater supplies.
Research has also shown that rainwater harvesting can reduce urban flooding, with significant results reported in the France-Italy cross-border coastal area.
Our own customers have reported excellent results from collecting rainwater. In fact, one customer, an extended-stay hotel in Virginia, asked to expand its rainwater harvesting system to take further advantage of the available rainfall.
As a leading provider of rainwater collection systems, Rainwater Management Solutions is well-situated to answer your questions about rainwater harvesting. Read on for the information you need.
Rainwater harvesting consists of collecting, pre-filtering, and storing rainwater from surfaces like rooftops, land, or rock catchments for later use. This ancient practice has been modernized for various purposes, including garden irrigation, drinking water, and groundwater recharge.
Rainwater harvesting helps the environment by reducing dependence on groundwater and municipal water supplies, decreasing stormwater runoff thus decreasing pollution of our waterways, and mitigating soil erosion. It also helps replenish the groundwater table.
Yes, harvested rainwater can be used for drinking, but it must be adequately filtered and treated to remove contaminants and pathogens. We offer excellent systems that can help ensure the safety of your collected rainwater.
A typical rainwater collection system includes a catchment area (like a rooftop), a conveyance system (gutters and downspouts), pre-filtration, a storage system (tanks or barrels), and often a post-tank treatment system for cleaning the water before use. Rainwater Management Solutions offers everything you need for collecting rainwater.
Embrace the power of rainwater harvesting — a simple yet effective way to conserve water, reduce your environmental footprint, and cut utility expenses. Whether you're looking to irrigate your garden, supply your household, or contribute to groundwater replenishment, we design our systems to meet your needs. Our range of products, from tanks and filters to sophisticated rainwater collection systems, are engineered for efficiency and ease of use. Plus, our expert team is here to guide you through every step, from choosing the right system to installation and maintenance. Contact us today and put the RMS difference to work for you.

 Off-The-Grid Rainwater Collection Systems
Living off-grid comes with its own unique set of advantages and challenges. For those seeking a new adventure or looking to reduce their carbon footprint... Read More
Off-The-Grid Rainwater Collection Systems
Living off-grid comes with its own unique set of advantages and challenges. For those seeking a new adventure or looking to reduce their carbon footprint... Read More  Rainwater Harvesting 101: Water Tank Overflow
Continuing our series of posts on Rainwater Harvesting 101, today we will look at using a water tank overflow... Read More
Rainwater Harvesting 101: Water Tank Overflow
Continuing our series of posts on Rainwater Harvesting 101, today we will look at using a water tank overflow... Read More  Unique Applications for Rainwater Harvesting
With the rise of sustainable business practices and the growing emphasis on renewables, there is a continuing need for the expansion... Read More
Unique Applications for Rainwater Harvesting
With the rise of sustainable business practices and the growing emphasis on renewables, there is a continuing need for the expansion... Read More